Abstract
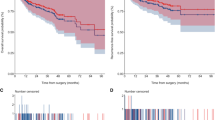
Robotic-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with urinary diversion is commonly performed in community hospitals. While little data exist on RARC outcomes in this setting, community hospitals may improve access to care for bladder cancer patients. We conducted a retrospective review of 76 patients who underwent RARC between 2006 and 2016 by two robotic-trained surgeons in two local community hospitals. A total of 76 patients (60 males and 16 females; ages 46–89) underwent RARC with extended pelvic lymphadenectomy and urinary diversion (69 ileal conduits, 7 neobladders) for muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma (79%), recurrent high-grade carcinoma (17%), unresectable tumor (2%), or refractory gross hematuria from chemotherapy (2%). Median-estimated surgical blood loss (EBL) was 400 mL, and median operating time was 386 min. Transfusion rate was 22% and median length of hospital stay was 6 days. Our 90-day complication rate was 47%, with no mortalities in the 90-day post-operative period. The majority of complications (58%) were Clavien grade 1–2. We observed a significant difference in incidence of complications among patients receiving neobladder vs. ileal conduit (p = 0.002). On pathology, zero patients had positive bladder specimen margins. Among 28 patients with at least 3-year follow-up, overall survival was 85.7%, and among 9 patients with at least 5-year follow-up, overall survival was 100%. Contrary to some studies, our findings suggest similar short-term surgical and pathologic outcomes for RARC performed in the community hospital setting compared to high volume centers. We defined several criteria for low volume centers to effectively and safely perform RARC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aron M (2015) Robotic radical cystectomy: so far, so good—what next? Eur Urol 67:361–362
Tang K (2009) Robotic vs. open radical cystectomy in bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 40:1399–1411
Leow J et al (2014) Propensity-matched comparison of morbidity and costs of open and robot-assisted radical cystectomies: a contemporary population-based analysis in the United States. Eur Urol 66:569–576
Gamboa A et al (2009) Pelvic lymph node dissection and outcome of robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder carcinoma. Robot Surg 3:7–12
Treiyer A et al (2012) Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: surgical and oncological outcomes. Int Braz J Urol 38:324–329
Khan M (2013) Long-term outcomes of robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Eur Urol 64:219–224
Nix J et al (2010) Prospective randomized controlled trial of robotic versus open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: perioperative and pathologic results. Eur Urol 57:196–201
Pruthi RS, Nielsen ME, Nix J, Smith A, Schultz H, Wallen EM (2010) Robotic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: surgical and pathological outcomes in 100 consecutive cases. J Urol 183:510–515
Kader A, Karim A (2013) Robot-assisted laparoscopic vs open radical cystectomy: comparison of complications and perioperative oncological outcomes in 200 patients. BJU Int 112:E290–E294
Niegisch G et al (2014) Perioperative complications and oncological safety of robot-assisted vs. open radical cystectomy. Urol Oncol 32:966–974
Maes A et al (2013) Comparison of robotic-assisted and open radical cystectomy in a community-based, non-tertiary health care setting. J Robot Surg 7:359
Azzouni F (2013) Current status of minimally invasive radical cystectomy: an outcome-based comparison. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 13:681–695
Novara G et al (2015) Systematic review and cumulative analysis of perioperative outcomes and complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 67:376–401
Xia L et al (2015) Robotic versus open radical cystectomy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(3):e0121032. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0121032
Li K et al (2013) Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies reporting early outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy. Cancer Treat Rev 39:551–560
Styn N et al (2012) Matched comparison of robotic-assisted and open radical cystectomy. Urology 79:1303–1308
Monn M et al (2014) National trends in the utilization of robotic-assisted radical cystectomy: An analysis using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Urol Oncol 32:785–790
Yu H et al (2012) Comparative analysis of outcomes and costs following open radical cystectomy versus robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: results from the US Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Eur Urol 61:1239–1244
Snow-Lisy D et al (2014) Robotic and laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: long-term oncologic outcomes. Eur Urol 65:193–200
Collins J et al (2014) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy: description of an evolved approach to radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 64:654–663
Wilson TG et al (2014) Best practices in robot-assisted radical cystectomy and urinary reconstruction: recommendations of the Pasadena Consensus Panel. Eur Urol 67:363–375
Raza S et al (2014) Oncologic outcomes following robot-assisted radical cystectomy with minimum 5-year follow-up: the Roswell Park cancer institute experience. Eur Urol 66:920–928
Lee R et al (2011) Cost-analysis comparison of robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy (RC) vs open RC. BJU Int 108:976–983
Martin A et al (2011) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy: a complete cost analysis. Urology 77:621–625
Gore JL, Saigal CS, Hanley JM, Schonlau M, Litwin MS (2006) Variations in reconstruction after radical cystectomy. Cancer 107(4):729–737
Hollenbeck BK, Dunn RL, Miller DC, Daignault S, Taub DA, Wei JT (2007) Volume-based referral for cancer surgery: informing the debate. J Clin Oncol 25(1):91–96
Casey MF, Wisnivesky J, Le VH et al (2016) The relationship between centralization of care and geographic barriers to cystectomy for bladder cancer. Bladder Cancer 2(3):319–327
Josephson D et al (2010) Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical cystoprostatectomy and extracorporeal continent urinary diversion: highlight of surgical techniques and outcomes. Int J Med Robot 6:315–323
Lau C et al (2012) Robotic assisted laparoscopic cystectomy in the octogenarian. Int J Med Robot 8:247–252
Studer U et al (1989) Three years’ experience with an ileal low pressure bladder substitute. BJU Int 63:43–52
Ahlering TE, Weinberg AC, Razor B (1991) Modified Indiana pouch. J Urol 145:1156–1158
Pruthi R et al (2003) Reducing time to oral diet and hospital discharge in patients undergoing radical cystectomy using a perioperative care plan. Urology 62:661–665
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Gore JL, Lai J, Setodji C, Litwin MS, Saigal CS (2009) Mortality increases when radical cystectomy is delayed more than 12 weeks: results from a seer medicare analysis. Cancer 115(5):988–996
Lee CT, Madii R, Daignault S, Dunn RL, Zhang Y, Montie JE, Wood DP (2006) Cystectomy delay more than 3 months from initial bladder cancer diagnosis results in decreased disease specific and overall survival. J Urol 175(4):1262–1267
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors ED and FS declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Informed consent
This retrospective study utilized only de-identified personal health data. At the time of indicated medical treatment, appropriate informed consent was obtained in accordance with the accepted standard of medical care.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DiLizia, E.M., Sadeghi, F. Surgical and pathological outcomes of robotic-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer in the community setting. J Robotic Surg 12, 337–341 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-017-0740-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-017-0740-y