Abstract
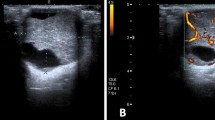
We report a rare case of Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) with multiple microliths in the bilateral parotid glands. A 41-year-old man presented to our department with mild pain in the region of the right parotid gland. The dental examination was negative except for the parotid regions. The right region was moderately swollen and the left mildly swollen. Plain radiography revealed multiple calculi in the bilateral parotid glands. Ultrasonography showed heterogenic parenchyma, with microliths and cystic lesions in the parotid glands and heterogenic echotexture in the submandibular glands. Immunologic tests and the Schirmer test confirmed the diagnosis of SS. As the patient had no classic symptoms of SS, the bilateral multiple microliths were the first sign, facilitating the final diagnosis. Early diagnosis of SS is highly relevant because the proper therapy can be initiated. Adequate follow-up and, especially, control of the disease activity by identifying the predictive factors, are the primary objectives of SS management, enabling personalized treatment of this malignant disease. This case is a good example of how detection of calcifications in the bilateral parotid glands by plain radiography can help diagnose SS at an early stage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoun G, Nasseh I, Berberi A. Evaluation of the oral component of Sjogren’s syndrome: an overview. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2016;6:278–84.
Rischmueller M, Tieu J, Lester S. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2016;30:189–220.
Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Pers JO, Marhadour T, Cochener B, Boisramé-Gastrin S, et al. Contribution of salivary gland ultrasonography to the diagnosis of Sjogren’s syndrome: toward new diagnostic criteria? Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:216–25.
Gaubitz M. Epidemiology of connective tissue disorders. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(Suppl 3):iii3–4.
Patel R, Shahane A. The epidemiology of Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:247–55.
Gadodia A, Bhalla AS, Sharma R, Thakar A, Parshad R. Bilateral parotid swelling: a radiological review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011;40:403–14.
Konstantinidis I, Paschaloudi S, Triaridis S, Fyrmpas G, Sechlidis S, Constantinidis J. Bilateral multiple sialolithiasis of the parotid gland in a patient with Sjögren’s syndrome. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2007;27:41–4.
Shimizu M, Yoshiura K, Nakayama E, Kanda S, Nakamura S, Ohyama Y, et al. Multiple sialolithiasis in the parotid gland with Sjogren’s syndrome and its sonographic findings: report of 3 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontology. 2005;99:85–92.
Tagnon BB, Theate I, Weynand B, Hamoir M, Coche EE. Long-standing mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the parotid gland: CT and MR imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:1563–5.
Carotti M, Salaffi F, Manganelli P, Argalia G. Ultrasonography and colour doppler sonography of salivary glands in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2001;20:213–9.
Salaffi F, Argalia G, Carotti M, Giannini FB, Palombi C. Salivary gland ultrasonography in the evaluation of primary Sjogren’s syndrome: comparison with minor salivary gland biopsy. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:1229–36.
Skopouli FN, Dafni U, Ioannidis JP, Moutsopoulos HM. Clinical evolution, and morbidity and mortality of primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2000;29:296–304.
Nocturne G, Mariette X. Sjogren syndrome-associated lymphomas: an update on pathogenesis and management. Br J Haematol. 2015;168:317–27.
De Vita S, Lorenzon G, Rossi G, Sabella M, Fossaluzza V. Salivary gland echography in primary and secondary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992;10:351–6.
Lindman JP, Woolley AL. Multiple intraparenchymal parotid calculi: a case report and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2003;82:615–7.
Ottaviani F, Galli A, Lucia MB, Ventura G. Bilateral parotid sialolithiasis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and immunoglobulin G multiple myeloma. Oral Sur Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontology. 1997;83:552–4.
Wickramasinghe A, Howarth A, Drage NA. Multiple bilateral parotid sialoliths in a patient with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT lymphoma) of the salivary glands. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontology. 2005;99:496–8.
Ohbayashi N, Yamada I, Yoshino N, Sasaki T. Sjögren syndrome: comparison of assessments with MR sialography and conventional sialography. Radiology. 1998;209:683–8.
Baldini C, Luciano N, Mosca M, Bombardieri S. Salivary gland ultrasonography in Sjogren’s syndrome: clinical usefulness and future perspectives. Isr Med Assoc J. 2016;18:193–6.
Hammenfors DS, Brun JG, Jonsson R, Jonsson MV. Diagnostic utility of major salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33:56–62.
Jonsson MV, Baldini C. Major salivary gland ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Sjogren’s syndrome: a place in the diagnostic criteria? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2016;42:501–17.
Diederich S, Wernecke K, Peters PE. Sialographic and sonographic diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Radiologe. 1987;27:255–61 (German).
Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Marhadour T, Pers JO, Boisramé-Gastrin S, Renaudineau Y, et al. Salivary gland ultrasonography improves the diagnostic performance of the 2012 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53:1604–7.
Siddiqui SJ. Sialolithiasis: an unusually large submandibular salivary stone. Br Dent J. 2002;193:89–91.
Rinast E, Gmelin E, Hollands-Thorn B. Digital subtraction sialography, conventional sialography, high-resolution ultrasonography and computed tomography in the diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Eur J Radiol. 1989;9:224–30.
Izumi M, Kise Y, Murata K, Murata A, Nakayama M, Ariji Y, et al. Multiple calcifications within the parotid gland of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Oral Sci Int. 2013;10:28–32.
Sun Z, Zhang Z, Fu K, Zhao Y, Liu D, Ma X. Diagnostic accuracy of parotid CT for identifying Sjogren’s syndrome. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:2702–9.
Theander E, Manthorpe R, Jacobsson LT. Mortality and causes of death in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1262–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Adrienn Dobai, Levente Pataky, and József Barabás declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements and informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. We read the Helsinki Declaration and have maintained its ethical standards. The patient has given informed consent to publish the case report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobai, A., Pataky, L. & Barabás, J. Multiple microlithiasis in bilateral parotid glands as the initial clinical manifestation of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Oral Radiol 34, 267–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-017-0294-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-017-0294-8