
Ben Bernanke, then Chairman of the Federal Reserve, told Congress in March 2007 that subprime was contained. He will rightfully be remembered in infamy for that, but that wasn’t the most egregious example of being wrong. Even putting it in those terms risks understating the problem and why it stubbornly lingers. Being really wrong is claiming that IOER will establish a floor for money market rates, and then finding out it actually doesn’t.
No, what policymakers did especially in the early crisis period was altogether worse; they demonstrated conclusively that though they shared this world with the rest of us, they inhabited and continue to inhabit a totally different planet.
Given the anniversary date and our human affinity for round numbers (ten years or a lost decade), there is a desire to revisit some of the worst of the list which happened just before August 9, 2007. My favorite has always been Bill Dudley, as I recounted last at the ninth anniversary of nothing being done:
As far as the issue of material nonpublic information that shows worse problems than are in the newspapers, I’m not sure exactly how to characterize that because I guess I wouldn’t know how to characterize how bad the newspapers think these problems are. [Laughter] We’ve done quite a bit of work trying to identify some of the funding questions surrounding Bear Stearns, Countrywide, and some of the commercial paper programs. There is some strain, but so far it looks as though nothing is really imminent in those areas.” [emphasis added]
He spoke those words, recorded for posterity, on August 7, 2007, at the regular FOMC policy meeting. As noted earlier today, both Countrywide and the whole commercial paper market would be decimated really within hours from his “inspiring” confidence.
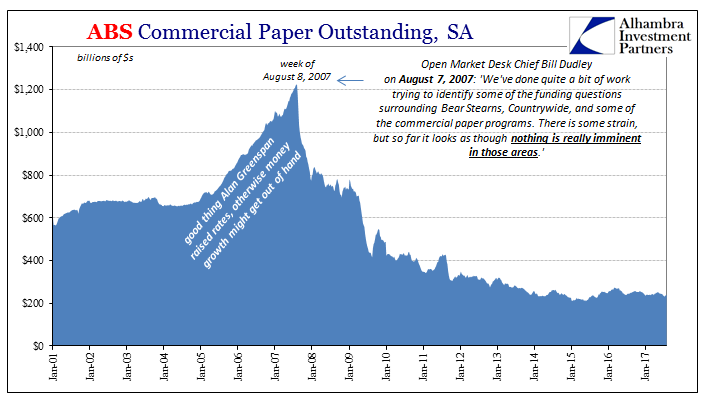
What really stands out is for Dudley to have been the one who said them, because as head of the Open Market Desk he had to be technically proficient in a way that the others could avoid (and why so often in its history policy discussions especially about these great things would often flow through whomever was the Open Market Desk chief at that moment in time). He proved still to be an empty suit like the rest, but he was always that much less of one. So if the best the Fed had to offer was so thoroughly unaware, is it any wonder what happened then and continues to happen now?
One day after Dudley’s private embarrassment, one Bank of England governor and future chief perhaps joined his level in the Hall of Fame of Famous Last Words. Meryn King remarked on August 8, 2007:
So far what we have seen is not a threat to the financial system. It’s not an international financial crisis.
He said these words at the behest of the ECB in front of the assembled press ostensibly to impart calm. Also noted earlier today, it was the European Central Bank that made the first crisis move the very next day in a record liquidity injection.

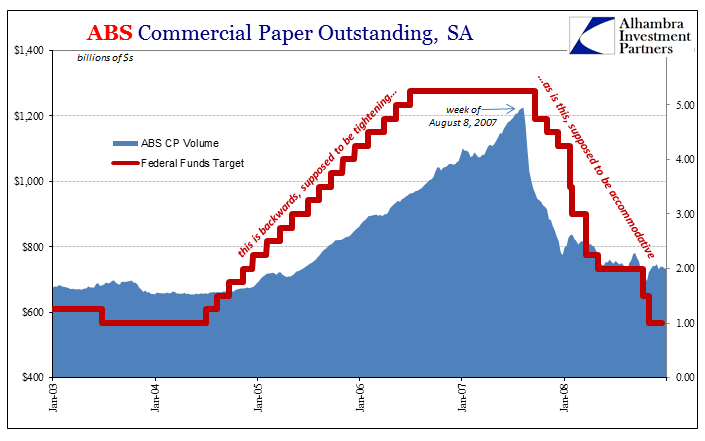
If officials didn’t realize what was happening monetarily, and they didn’t, there was obviously no way for them to predict what would happen economically. One follows the other, so if you think the monetary system is infected only with raw, mistaken emotion to be easily cleaned up by genius and effective policy intervention, then you will likewise believe the consequences to the real economy quite small and completely manageable.
In its bland policy statement that accompanied the August 7, 2007, policy meeting, the FOMC voted affirmatively (and quite purposefully) for this language:
Financial markets have been volatile in recent weeks, credit conditions have become tighter for some households and businesses, and the housing correction is ongoing. Nevertheless, the economy seems likely to continue to expand at a moderate pace over coming quarters, supported by solid growth in employment and incomes and a robust global economy. [emphasis added]
I could go on and on with these examples, but you get the point; the main of which is to paraphrase one religious sentiment. No Money, No Economy; Know Money, Know Economy. These last ten years have proved beyond any doubt in gross empirical fashion policymakers and economists (redundant) don’t get either money or economy.

Stay In Touch