An Alaska Native group decided to make a video game. It's like nothing you've ever played before.
One of the most groundbreaking, critically acclaimed, and delightful video games of 2014 began in a highly unlikely place — Anchorage, Alaska.
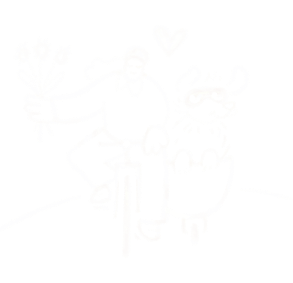
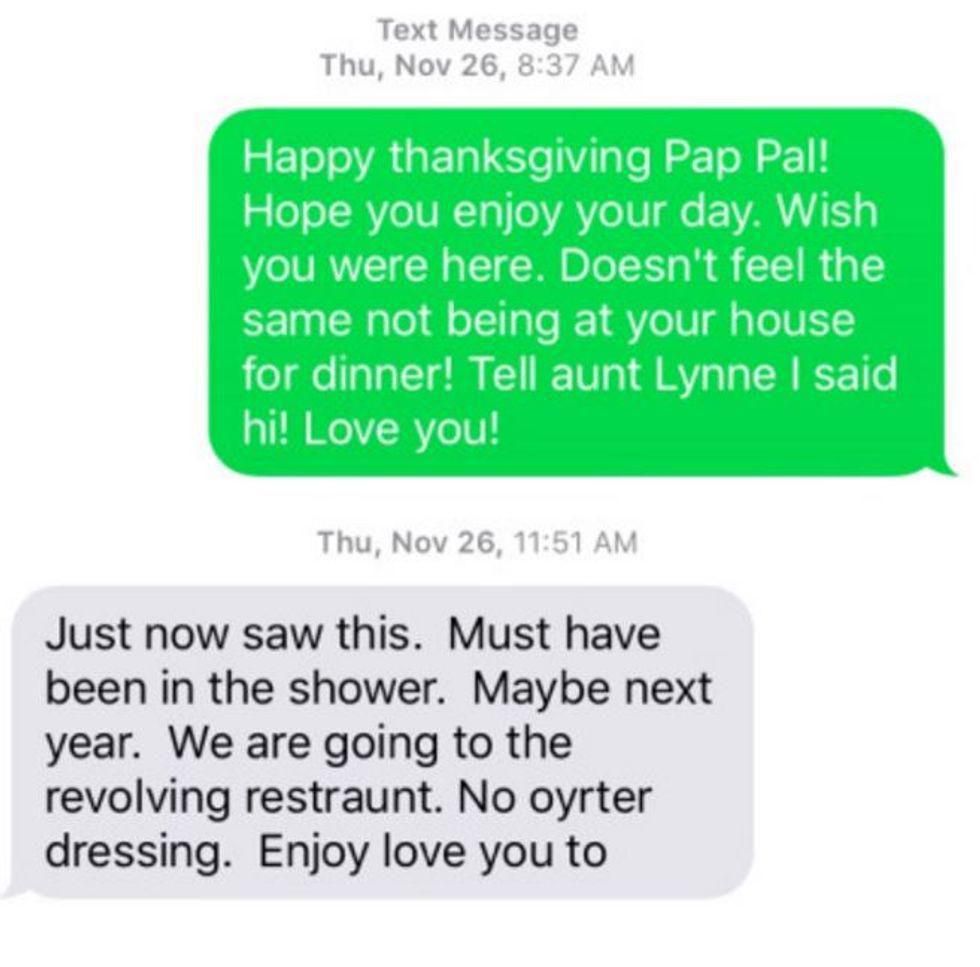
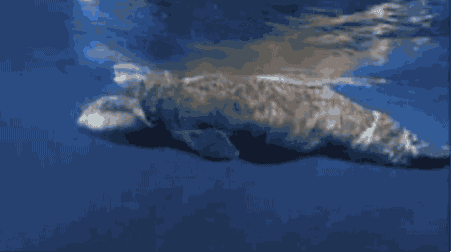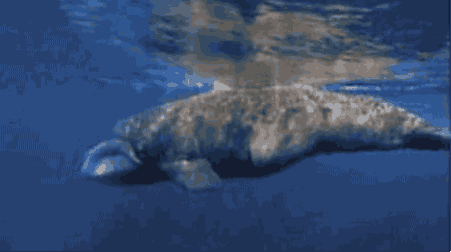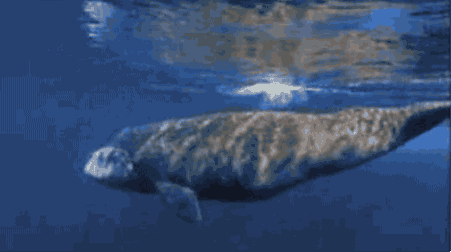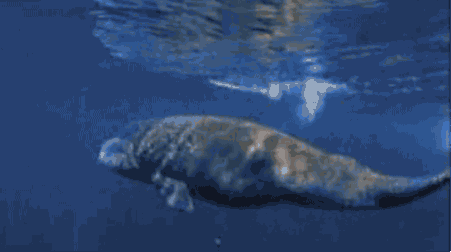
A scene from "Never Alone." Photos by North One Games/E-Line Media.
It's called "Never Alone" (or "Kisima Ingitchuna"). And it wasn't developed by Nintendo, Electronic Arts, Ubisoft, or any of the other big game studios.
It was the brainchild of the Cook Inlet Tribal Council (CITC) — a nonprofit community support organization for Alaska Natives and their families.
Many Alaska Native communities are struggling to hold on to their identities in the 21st century.
As more and more Alaska Natives move out of traditional communities and into urban areas, indigenous languages are disappearing — and with them, traditional knowledge. Many don't have a choice because climate change threatens to erode and, in some cases, even destroy native towns and villages around the state.
For many, life in Alaska's cities is hardly easy. According to Amy Fredeen, executive vice president and chief financial officer of the CITC, Alaska Native youth in Anchorage are plagued by high dropout and suicide rates. Passing traditional knowledge down under these conditions becomes all the more challenging.
The council saw "Never Alone" as both a way of becoming more financially self-sufficient and a necessary new method of transferring cultural knowledge from one generation to the next.
"We saw video games as a way to connect to our youth in a place where they're already at," Fredeen told Upworthy. The group also hoped that sales of the video game would help reduce their dependence on federal grant money.
There was a problem, however: No one on the CITC had ever made a video game before.
Undaunted, the council cold-called E-Line Media, a Seattle-based entertainment and video game development company with a message: "Come to Anchorage."
"What was funny is they actually came up and tried to talk us out of it."
According to Fredeen, E-Line urged the council to approach the project with caution: Video game development is a highly risky business and particularly challenging for a nonprofit with limited cash supplies.
But the group was determined — and the developers were impressed.
E-Line signed on. And off they went.
The team started by analyzing how indigenous characters were typically portrayed in video games. What they found was upsetting — and unsurprising.
"It ran the gamut from being terrible stereotypes to just appropriation," Fredeen said.
The group found that not only were native video game characters exceedingly rare, but when they did appear, it was often as sidekicks exhibiting a mishmash of cultural signifiers cobbled together from various and unrelated communities or, worse, as one-dimensional villains.
"Some of them were really almost obscene," Fredeen said.
In contrast, "Never Alone" features an Alaska Native main character and is based largely on a traditional Iñupiaq story.
E-Line chief creative officer Sean Vesce teaches Minnie Gray, an Alaska Native elder, storyteller, and consultant on the game, how to play.
Nuna, the game's hero, teams up with an arctic fox to find the source of the blizzard that's threatening her community. Players explore themes of resourcefulness, cooperation, and the transfer of knowledge from one generation to the next through the beautifully rendered gameplay.
"When I saw that come to life on screen, when they were using the scrimshaw in an animated way to tell a story, it brought tears to my eyes." — Amy Fredeen
E-Line credits the game's part-Iñupiaq lead writer, Ishmael Hope, for helping ensure that Alaska Native voices were front and center in the development process.
“We want to be culturally appropriate without cultural appropriation," Matt Swanson, one of the game's producers told Upworthy.
That meant checking their egos at the door and questioning some assumptions they didn't even realize they had.
According to Swanson, the original villain of the game was slated to be a raven before their collaborators pointed out that wouldn't make sense in an Alaska Native context.
"As Westerners, we have lots of stories where [the raven] is a trickster character, and things like that. And they pushed back on that and said, 'Look, that's not really culturally appropriate. The raven in our culture is a much more sort of sacred character.'"
It was a surprise to the E-Line team, which highlighted the importance of listening and their role as students in the story development process.
In addition to the main game, "Never Alone" features hours of documentary footage of Alaska Native elders and community members sharing traditional stories, explaining customs, and passing down knowledge.
The team was initially worried that the footage — which the player has the option of watching — would disrupt the gameplay but later received tons of positive feedback on the feature.
For Fredeen, the moment she knew "Never Alone" was going to be something special was when she saw the first cutscene — rendered entirely in serialized scrimshaw.
Scrimshaw is a traditional form of bone or ivory carving. According to Fredeen, while scrimshaw today is most often done in single panel, it was traditionally used in Alaska Native communities as a multi-panel, serial storytelling device.
"When I saw that come to life on screen, when they were using the scrimshaw in an animated way to tell a story, it brought tears to my eyes," Fredeen said. "The instant I saw that, I knew the team was listening to who we were as a people and how we really connected with each other."
The game debuted to terrific reviews and has since won some very big awards.
Minnie Gray in the recording studio.
Its effects are being felt far beyond Alaska's borders as well.
"After the game launched, we've been getting this incredible response from people of all different backgrounds on how getting to see an indigenous main character in a game, and seeing cultural representation in a game has resonated with them," Swanson said.
For Fredeen, the importance of that representation can't be overstated and was evident from the first time she saw a group of Alaska Native youth encounter the game.
"When they saw the video game on the screen, and when they saw a character that looked like them and the dress was familiar to them, and they saw their community members on the video with the video game, you could just see the pride on their faces."
The game is expected to make money — a big deal in the video game world — and the team continues to be impressed with its success.
“It's been amazing all around," Fredeen said.
"People just get excited in Alaska," she added. "... They're excited to see something that was made with Alaskans."