Abstract
Introduction
Hiccups caused by a neoplasm in the spinal cord are rare.
Materials and methods
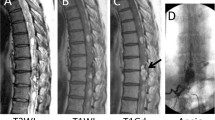
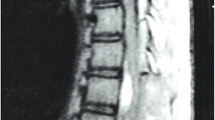
We report a case of intractable hiccups caused by syringobulbia and syringomyelia associated with cervical intramedullary spinal hemangioblastoma, which was successfully treated by surgical excision. A 60-year-old man was referred from the neurology department after presenting with hiccups for 1 year. The hiccups were aggravated 3 months ago and were sustained during eating or sleeping. Several doctors administered a muscle relaxant and an anticonvulsant, but they were ineffective. Spinal MRI revealed a huge syringomyelia from C2 to T2, associated with a highly enhancing intramedullary mass lesion at the C5 level. The hiccups were ceased after removal of the tumor through a right hemilaminectomy. The pathology of the specimen was hemangioblastoma. The size of the syringobulbia and syringomyelia decreased markedly on MRI checked 5 months after surgery.
Conclusions
Intractable hiccups can be caused by syringobulbia associated with an intramedullary cord tumor in the cervical area and possible mechanisms of hiccups were reviewed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seker MM, Aksoy S, Ozdemir NY, Uncu D, Civelek B, Akinci MB, Zengin N (2012) Successful treatment of chronic hiccup with baclofen in cancer patients. Med Oncol 29:1369–1370. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9910-3
Calsina-Berna A, Garcia-Gomez G, Gonzalez-Barboteo J, Porta-Sales J (2012) Treatment of chronic hiccups in cancer patients: a systematic review. J Palliat Med 15:1142–1150. doi:10.1089/jpm.2012.0087
Gilani SM, Danforth RD (2012) Intractable hiccups: a rare presentation of phrenic nerve schwannoma. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 129:331–333. doi:10.1016/j.anorl.2012.01.001
Fodstad H, Nilsson S (1993) Intractable singultus: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Br J Neurosurg 7:255–260
Seki T, Hida K, Lee J, Iwasaki Y (2004) Hiccups attributable to syringobulbia and/or syringomyelia associated with a Chiari I malformation: case report. Neurosurgery 54:224–226 (discussion 226–227)
Bor S, Mandiracioglu A, Kitapcioglu G, Caymaz-Bor C, Gilbert RJ (2005) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in a low-income region in Turkey. Am J Gastroenterol 100:759–765. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41065.x
Chang YY, Chen WH, Liu JS, Shih PY, Chen SS (1993) Intractable hiccup caused by medulla oblongata lesions. J Formos Med Assoc 92:926–928
Sugimoto T, Takeda N, Yamakawa I, Kawai H, Tanaka Y, Sakaguchi M, Osawa N, Uzu T, Kashiwagi A (2008) Intractable hiccup associated with aseptic meningitis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 17:152–153. doi:10.1177/0961203307085253
Delevaux I, Andre M, Marroun I, Lamaison D, Piette JC, Aumaitre O (2005) Intractable hiccup as the initial presenting feature of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 14:406–408
Eckardt VF (2001) Clinical presentations and complications of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 11:281–292
Funakawa I, Hara K, Yasuda T, Terao A (1993) Intractable hiccups and sleep apnea syndrome in multiple sclerosis: report of two cases. Acta Neurol Scand 88:401–405
Lewis JH (1985) Hiccups: causes and cures. J Clin Gastroenterol 7:539–552
Samuels L (1952) Hiccup; a ten year review of anatomy, etiology, and treatment. Can Med Assoc J 67:315–322
Pollack MJ (2003) Intractable hiccups: a serious sign of underlying systemic disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 37:272–273
Askenasy JJ (1992) About the mechanism of hiccup. Eur Neurol 32:159–163
Barriocanal Barriocanal AM, Vaque Cabanas A, Perez-Andres R, Olive Marques A (2005) Hiccups crisis following paramethasone intraarticular injection. Med Clin (Barc) 125:158
Errante D, Bernardi D, Bianco A, Zanatta N, Salvagno L (2005) Recurrence of exhausting hiccup in a patient treated with chemotherapy for metastatic colon cancer. Gut 54:1503–1504. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.071704
Katelaris PH (2003) Helicobacter pylori hiccup. Intern Med J 33:398 (author reply 398–399; discussion 399)
Misu T, Fujihara K, Nakashima I, Sato S, Itoyama Y (2005) Intractable hiccup and nausea with periaqueductal lesions in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 65:1479–1482. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000183151.19351.82
Park MH, Kim BJ, Koh SB, Park MK, Park KW, Lee DH (2005) Lesional location of lateral medullary infarction presenting hiccups (singultus). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:95–98. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.039362
Nagayama T, Kaji M, Hirano H, Niiro M, Kuratsu J (2004) Intractable hiccups as a presenting symptom of cerebellar hemangioblastoma. Case report. J Neurosurg 100:1107–1110. doi:10.3171/jns.2004.100.6.1107
Li ML, Gupta A, Thomas P, Richards AJ (2000) Basilar artery aneurysm: an unusual cause of intractable hiccups. Hosp Med 61:868–869
Dickerman RD, Jaikumar S (2001) The hiccup reflex arc and persistent hiccups with high-dose anabolic steroids: is the brainstem the steroid-responsive locus? Clin Neuropharmacol 24:62–64
Calvo E, Fernandez-La Torre F, Brugarolas A (2002) Cervical phrenic nerve block for intractable hiccups in cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:1175–1176
Kumral E, Acarer A (1998) Primary medullary haemorrhage with intractable hiccup. J Neurol 245:620–622
Lee KH, Moon KS, Jung MY, Jung S (2014) Intractable hiccup as the presenting symptom of cavernous hemangioma in the medulla oblongata: a case report and literature review. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 55:379–382. doi:10.3340/jkns.2014.55.6.379
Payne BR, Tiel RL, Payne MS, Fisch B (2005) Vagus nerve stimulation for chronic intractable hiccups. Case report. J Neurosurg 102:935–937. doi:10.3171/jns.2005.102.5.0935
Suzukawa K, Amoh M, Nakamura Y, Yasuma Y, Kurokawa S (2000) Spontaneous occlusion of a dissecting aneurysm in the shape of “two dumplings on a skewer” at righ posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA): report of a case and neuroradiological findings. No Shinkei Geka 28:561–567
Al Deeb SM, Sharif H, Al Moutaery K, Biary N (1991) Intractable hiccup induced by brainstem lesion. J Neurol Sci 103:144–150
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund and approved by the Institutional Review Board with informed consent of the patient.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, J.H., Im, SB., Shin, DS. et al. Intractable hiccups caused by syringobulbia and syringomyelia associated with intramedullary spinal hemangioblastoma. Eur Spine J 24 (Suppl 4), 614–618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3822-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3822-4