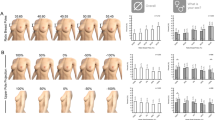
Abstract
Background
Breast hypertrophy can cause a variety of symptoms and affect lifestyle and quality of life. Breast reduction, being the most effective treatment, is sometimes difficult to establish as standard treatment in obese patients (difficulties to differentiate symptoms from macromastia or from obesity, higher rate of complications).
Aim
To evaluate the effect of reduction mammaplasty (quality of life and symptoms) in obese patients comparing with non-obese.
Methods
This is a prospective study of patients undergoing reduction mammaplasty. Patients were allocated in non-obese (BMI < 29) and obese (BMI > 30). Demographic data, comorbidities, specific symptoms questionnaire, data from the surgical procedure, Spanish version of the Health-Related Quality of Life (SF-36) questionnaire, complications and sequels were recorded and collected before the operation and at 1 month and 1 year after. Chi-square, Fisher’s exact t test, McNemar, Mann–Whitney U and Kruskal–Wallis tests were used for statistical analysis.
Results
One hundred twenty-one consecutive patients were operated on; 54 (44.6 %) obese and 67 (55.4 %) non-obese. The average age of patients was 40.7 (18–78), average volume of resected tissue was 1.784 g (401–5.790), and average hospital stay was 2.94 days (1–11). There were no differences between obese and normal BMI patients with regard to length of hospital stay, complications, sequels, or reoperations. Symptoms improved in both groups. Physical and mental components of the SF-36 improved at 1 year in both groups (p < 0.001). The mental health component improved at 1 month (p < 0.001) in both groups.
Conclusions
Obese patients should be considered for reduction mammaplasty surgery in the same way as women of normal weight.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each submission to which Evidence-Based Medicine rankings are applicable. This excludes Review Articles, Book Reviews, and manuscripts that concern Basic Science, Animal Studies, Cadaver Studies, and Experimental Studies. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. ASPS Recommended Insurance Coverage Criteria for Third-Party Payers, Reduction Mammaplasty. Position Paper approved by the ASPS Board of Directors 2002. http://www.plasticsurgery.org/Documents/medical-professionals/health-policy/key-issues/Recommended-Insurance-Coverage-Criteria.pdf
Kerrigan CL, Collins ED, Striplin D, Kim HM, Wilkins E, Cunningham B, Lowery J (2001) The health burden of breast hypertrophy. Plast Reconstr Surg 108(6):1591–1599
Benditte-Klepetko H, Leisser V, Paternostro-Sluga T, Rakos M, Trattnig S, Helbich T (2007) Hypertrophy of the breast: a problem of beauty or health? J Womens Health 16(7):1062–1069
Mello AA, Domingos NO, Miyazaqui MC (2010) Improvement in quality of life and self-esteem after breast reduction surgery. Aesthet Plast Surg 34:59–64
Dafydd H, Roehl KR, Phillips LG, Dancey A, Peart F, Shokrollahi K (2011) Redefining gigantomastia. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64:160–163
Dancey A, Khan M, Dawson J, Peartr F (2008) Gigantomastia, a classification and review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:493–502
Eggert E, Schuss R, Edsander-Nord A (2009) Clinical outcome, quality of life, patient satisfaction and aesthetic results after reduction mammaplasty. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 43:201–206
Chen CL, Shore AD, Johns R, Clark JM, Manahan M, Makary MA (2011) The impact of obesity on breast surgery complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 128(5):395–420
Manahan MA, Buretta KJ, Chang D, Mithani SK, Mallalieu J, Shermak MA (2015) An outcomes analysis of 2142 breast reduction procedures. Ann Plast Surg 74(3):289–292
Shah R, Al Ajam Y, Stott D, Kang N (2011) Obesity in mammaplasty: a study of complications following breast reduction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64:508–514
Gamboa-Bobadilla GM, Killingsworth C (2008) Large-volume reduction mammaplasty: the effect of body mass index on postoperative complications. Ann Plast Surg 58:246–249
World Health Organization. BMI classification. http://apps.who.int/bmi/index.jsp?introPage=intro_3.html
Alonso J, Prieto L, Antó JM (1995) Versión Española del cuestionario de salud SF-36 Health Survey (Cuestionario de Salud SF-36): un instrumento para medir los resultados clínicos. Med Clin (Barc) 104(20):771–776
Setälä L, Papp A, Joukainen S, Martikainen R, Berg L, Mustonen P, Härmä M (2009) Obesity and complications in breast reduction surgery: are restrictions justified? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:195–199
Wagner DS, Alfonso DR (2005) The influence of obesity and volume of resection on success in reduction mammaplasty: an outcomes study. Plast Reconstr Surg 115:1034–1038
Cunningham BL, Gear AJ, Kerrigan CL, Collins ED (2005) Analysis of breast reduction complications derived from the BRAVO study. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(6):1597–1604
Hunter-Smith DJ, Smoll NR, Marne B, Maung H, Findlay MW (2012) Comparing breast-reduction techniques: time-to-event analysis and recommendations. Aesthet Plast Surg 36(3):600–606
Roehl K, Stirling-Craigh E, Gomez V, Phillips L (2008) Breast reduction: safe in morbidly obese? Plast Reconstr Surg 122(2):370–378
Lejour M (1993) Vertical mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 92(5):985–986
Finger RE, Vasquez B, Drew S, Given K (1989) Superomedial pedicle technique of reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 83(3):471–478
Strombeck JO (1960) Reduction mammaplasty. A report on a new technique based on the two-pedicle procedure. Br J Plast Surg 13:79–90
Jones S, Bain J (2001) Review of data describing outcomes that are used to asses changes in quality of life after reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 108:62–67
O’Blenes CA, Delbridge CL, Miller BJ, Pantelis A, Morris SF (2006) Prospective study of outcomes after reduction mammaplasty: long-term follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(2):351–358
Rogliani M, Gentile P, Labardi L, Donfrancesco A, Cervelli V (2009) Improvement of physical symptoms after breast reduction surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:1647–1649
Singh KA, Pinell XA, Losken A (2010) Is reduction mammaplasty a stimulus for weight loss and improved quality of life. Ann Plast Surg 64(5):585–587
Brown JR, Holton LH, Chung TL, Slezak S (2008) Breast feeding, self-exam, and exercise practice before and after reduction mammoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 61:375–379
Chadbourne EB, Zhang S, Gordon MJ, Ro EY, Ross SD, Schnur PL, Schneider Redden PR (2001) Clinical outcomes in reduction mammaplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies. Mayo Clin Proc 76(5):503–510
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with regard to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güemes, A., Pérez, E., Sousa, R. et al. Quality of Life and Alleviation of Symptoms After Breast Reduction for Macromastia in Obese Patients: Is Surgery Worth It?. Aesth Plast Surg 40, 62–70 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0601-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0601-x